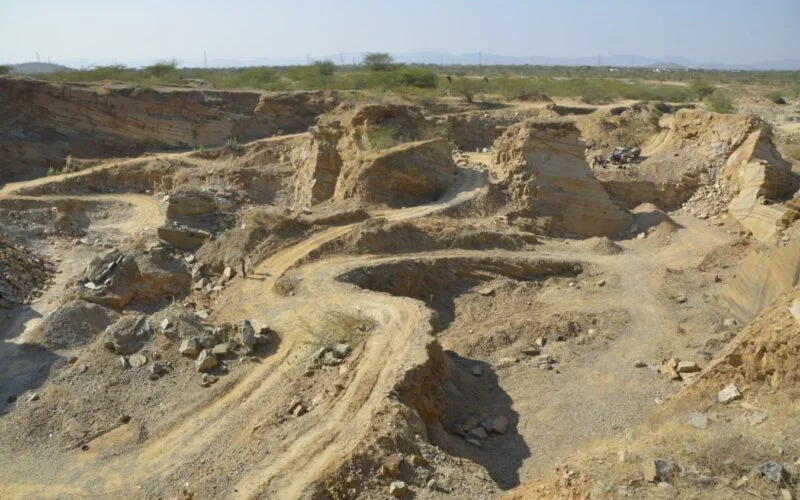
The Supreme Court of India has not issued a complete ban on mining in the Aravalli Hills. However, they have taken several steps to restrict and regulate mining activities in this ecologically sensitive region due to several concerns:
- Environmental Degradation: The Aravalli Hills act as a natural barrier protecting the fertile plains of North India from desertification. Excessive mining can lead to deforestation, soil erosion, and disruption of water sources. The Aravalli Range is rich in natural resources and serves as check to the growth of the western desert.
- Biodiversity Loss: The Aravallis are home to diverse flora and fauna, some of which are endangered. Mining activities can destroy habitats and threaten these species.
- Illegal Mining: Despite existing regulations, illegal mining has been a persistent problem in the Aravallis. This unregulated activity causes even greater environmental damage.
Supreme Court’s Actions:
- Halt on New Leases: In 2018, the Supreme Court ordered a halt on granting new mining leases in four states bordering the Aravallis: Rajasthan, Haryana, Gujarat, and Madhya Pradesh. This aimed to prevent further expansion of mining activity.
- Mapping and Scrutiny: The court directed the states to map the mining areas within the Aravallis and scrutinize existing mining leases to ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
- Focus on Sustainability: The court emphasized the need for sustainable practices in the region, encouraging responsible mining methods that minimize environmental impact.
Challenges and Concerns:
- Livelihoods: A complete ban on mining could affect the livelihoods of people who depend on the mining industry for work.
- Economic Impact: Mining can contribute to the economic development of the region. Finding a balance between economic needs and environmental protection is crucial.
The situation in the Aravalli Hills is complex, with competing interests at play. The Supreme Court’s actions aim to strike a balance by curbing illegal practices and promoting responsible mining practices that minimize environmental damage. It’s an ongoing process with the ultimate goal of protecting this ecologically significant region.
The Aravalli Hills stretch majestically across Rajasthan, Gujarat, Haryana, and Delhi, forming a vital ecological spine for the region. Their importance to the ecosystem and environment is multifaceted, playing a crucial role in:
Climate Regulation and Water Security:
- Natural Barrier: The Aravallis act as a natural barrier, protecting the plains of North India from the harsh Thar Desert winds and minimizing desertification. They create a rain shadow effect, forcing moisture-laden monsoon winds to rise and release precipitation on the windward side.
- Water Source: The Aravalli range is home to the headwaters of numerous rivers and streams, including the Luni, Sabarmati, and Mahi rivers. These rivers provide crucial freshwater resources for irrigation, drinking water, and maintaining ecological balance.
- Groundwater Recharge: The Aravalli hills act like giant sponges, absorbing rainwater and replenishing groundwater aquifers. This stored water sustains surrounding regions during dry seasons.
Biodiversity Hotspot:
- Rich Habitat: The Aravallis boast a rich tapestry of flora and fauna, with diverse vegetation zones ranging from dry deciduous forests to scrublands. This diverse habitat provides a sanctuary for numerous species, some of which are endangered.
- Endangered Species: The hills are home to critically endangered animals like the Great Indian Bustard, Caracal, Striped Hyena, and various reptiles and birds. Protecting the Aravallis is vital for the survival of these unique species.
Livelihoods and Economic Benefits:
- Forestry and Agriculture: The Aravalli ecosystem supports communities dependent on forestry and agriculture. The hills provide timber, non-timber forest products (medicinal plants, fruits), and regulate soil fertility, benefiting agricultural practices in surrounding areas.
- Tourism and Recreation: The scenic beauty and historical significance of the Aravallis attract tourists, generating revenue for the region and supporting ecotourism initiatives.
The Threats and the Need for Conservation:
Despite their immense importance, the Aravallis face significant threats:
- Illegal Mining: Unregulated mining activities lead to deforestation, soil erosion, and water table depletion.
- Urbanization and Encroachment: Rapid urbanization and construction projects pose a threat to the natural habitat and ecological balance.
- Overgrazing: Unsustainable grazing practices can damage vegetation and contribute to soil erosion.
Conservation Efforts:
- Protected Areas: Several national parks and wildlife sanctuaries within the Aravallis offer protection to flora and fauna.
- Sustainable Practices: Promoting responsible mining methods and afforestation initiatives are crucial for long-term sustainability.
- Community Awareness: Educating local communities about the importance of the Aravallis and fostering a sense of ownership is essential for conservation efforts.
Due to the widespread concern regarding the Aravalli Hills, there isn’t a single NGO solely responsible for the protection movement. Several environmental NGOs and activist groups are actively involved in raising awareness and advocating for the Aravalli Hills. Here are a few prominent examples:
- Himalayan Environment and Conservation Organisation (HECO): This NGO focuses on environmental issues in the Himalayas and the Aravallis. They have been involved in legal battles against illegal mining and raising public awareness about the ecological significance of the Aravallis.
- Aravalli Bachao Citizen Movement: This citizen-led movement actively campaigns for the protection of the Aravallis. They organize protests, awareness campaigns, and legal interventions to safeguard the environment.
- Wildlife SOS: This organization, known for its wildlife conservation efforts, also works towards protecting the habitat of endangered species in the Aravalli Hills.
In addition to these, numerous other NGOs and environmental groups across India play a role in the Aravalli Hills protection movement. Here are some resources that can help you learn more:
- Save Aravali: This environmental organization based in Haryana focuses on protecting the Aravallis. Their website (https://www.savearavali.org/) might provide insights into current initiatives.
- Down To Earth Magazine: This Indian environmental magazine frequently covers issues related to the Aravalli Hills. Their website (https://www.downtoearth.org.in/) might have articles highlighting NGOs involved in the movement.
Remember, the Aravalli Hills protection movement is a collective effort by various stakeholders. By exploring the resources mentioned above, you can gain a broader understanding of the organizations and individuals working tirelessly to preserve this vital ecological region.
Conclusion:
The Aravalli Hills are an ecological treasure, playing a critical role in the environmental well-being of the region. Protecting and restoring this fragile ecosystem is vital for ensuring a healthy climate, safeguarding biodiversity, and sustaining livelihoods for generations to come.
Feature Image source: WildHawk

 Add to favorites
Add to favorites